|
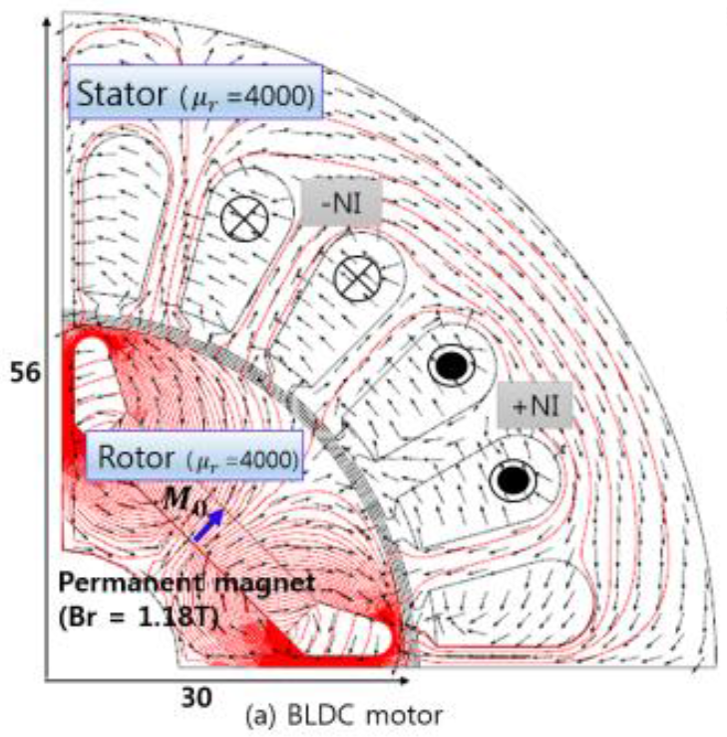
Jin-Hyun Choi, Changseob Kwak, Hong-Soon Choi, Hyungpyo Kim, Se-Hee Lee," Mechanical Deformation and Body Force Density Due to the Generalized Korteweg–Helmholtz Force Density Method Employing the Virtual Air-Gap Scheme", IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 52, NO. 7, JULY 2016. A generalized Korteweg-Helmholtz
force density method (GKH) was implemented incorporating the virtual airgap
scheme and the Finite Element Method (FEM) for evaluating magnetic body force
density and mechanical deformation. Until now, several generalized force
calculation methods adopting the virtual airgap
scheme have been developed and successfully applied to contact and mechanical
deformation problems. The Korteweg-Helmholtz
force density method (KH) is well known and can be derived with theoretical
completeness, and it can be changed into the tensor formulation for calculating
force density and total force on the electromagnetic body. This KH is
numerically stable compared with the conventional Maxwell stress tensor method
(MX) because it adopts the tensor difference at an interface. However, the KH
also has difficulty calculating the contact force and body force density.
Therefore, here, we developed the GKH force density method employing the
virtual airgap
scheme. Additionally, the mechanical deformation was tested quantitatively and
compared with those from conventional force calculation methods including the
MX, the KH, the equivalent magnetic charge method, and the Kelvin force density
method. To verify the mechanical deformation due to the GKH, we implemented the
GKH and compared the mechanical deformations between the several numerical
results.
|



